Troubleshooting Eaton Transmission Gears & Shafts
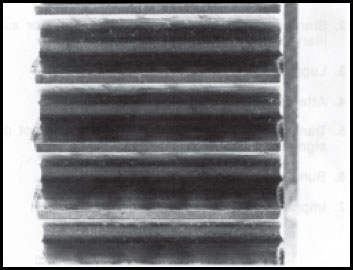
Clashing Gears
Snubbing and clashing gears while shifting are frequent abuses to which unsynchronized transmissions are subjected. Light snubbing will do little damage. The real damage is done by the hard clash shift caused by engaging gears which are far out of synchronization. This can break pieces of metal from the ends of the clutching teeth. Clashing gears can be traced to one of three causes:
Snubbed Clutching Gear Teeth
1. Improper Shifting
This applies to drivers who are not familiar with the shift pattern or have not learned the RPM spread between shifts.
2. Clutch
Clashing when starting up in first or reverse gear can be caused by insufficient clutch clearance or a dragging clutch not releasing properly. This makes the transmission countershafts and mainshaft gears continue rotating while the clutch pedal is depressed. Clashing results when the nonrotating sliding clutch is forced to mesh with a rotating mainshaft gear. Double clutching during lever shifts will also reduce snubbing and clashing.
3. Inertial Force
Countershafts and mainshaft gears usually take from 3 to 5 seconds to stop rotating after the clutch has been disengaged. Attempting to mesh a clutch gear with a mainshaft gear before the mainshaft gear stops will result in clashing. If the transmission is not equipped with a clutch brake or countershaft brake, it is necessary to pause a few seconds after depressing the clutch pedal before attempting initial engagement of the transmission.
Manufacturing Marks
Sometimes gears are replaced or thought to be defective because of marks left on the gear by manufacturing processes. These blemishes, however, do not contribute to gear failure and the gear should not be replaced because of these marks.
Hob Marks
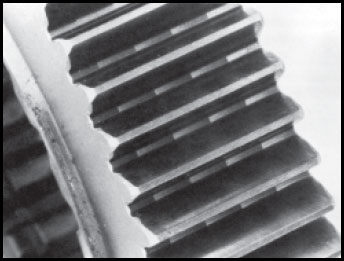
These are cutting marks or lines formed during the initial cutting of the gear teeth. Hob marks on the tooth face will be removed by the shaving process, but hob marks in the root of the tooth will most likely remain, and may be found even on gears with much wear on them.
Shaving Marks
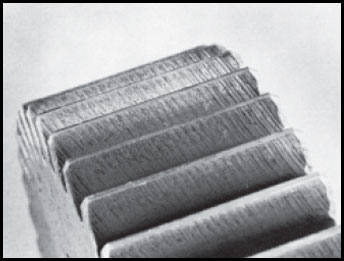
The shaving operation leaves distinct diagonal marks on the face of the gear tooth. These marks can be distinguished from scoring marks by the fact they are diagonal, while scoring marks are more nearly vertical. Most shaving marks are removed during normal gear operation.
Gear Rattle at Idle
Mainshaft gears are designed to have a specified amount of axial clearance which allows them to rotate freely on the mainshaft. The amount of clearance is governed by the use of washers. A rough idling engine can set up vibrations, causing the mainshaft gears to rattle as they strike mating gears. This condition can usually be cured by improving the idling characteristics of the engine. Tolerance washers may have to be changed to bring the axial gear clearance to within tolerance on high mileage units. See the service manual for procedure and specifications.
Shaft Twist and Fracture
Failure of transmission shafts through fracturing or twisting is caused when stresses are imposed on them which are greater than they were designed to withstand. The main causes for these failures are:
- Improper clutching techniques.
- Starting in too high of gear.
- Lugging.
- Attempting to start with brakes locked.
- Transmission used for application it was not designed to withstand.
- Bumping into dock when backing.
- Improper mounting of adjustable 5th wheel.
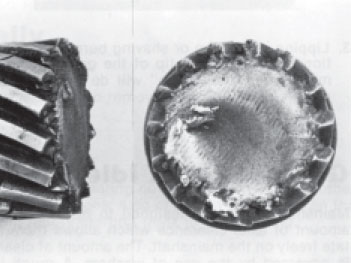
Fractured Mainshaft
As with gear teeth, shafts may fracture as a result of fatigue or impact.
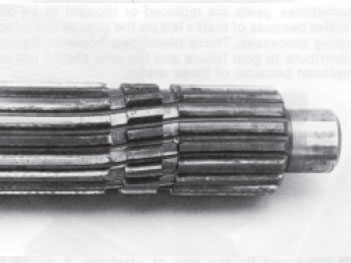
Twisted Mainshaft
Loads not severe enough to cause shaft fractures may cause the shaft to twist.
Any transmission part you need we have it! Same day shipping available, worldwide.
NEED FREE SUPPORT FROM ONE OF OUR EXPERTS?